Flamingos and Their Role in Wetland Ecosystems
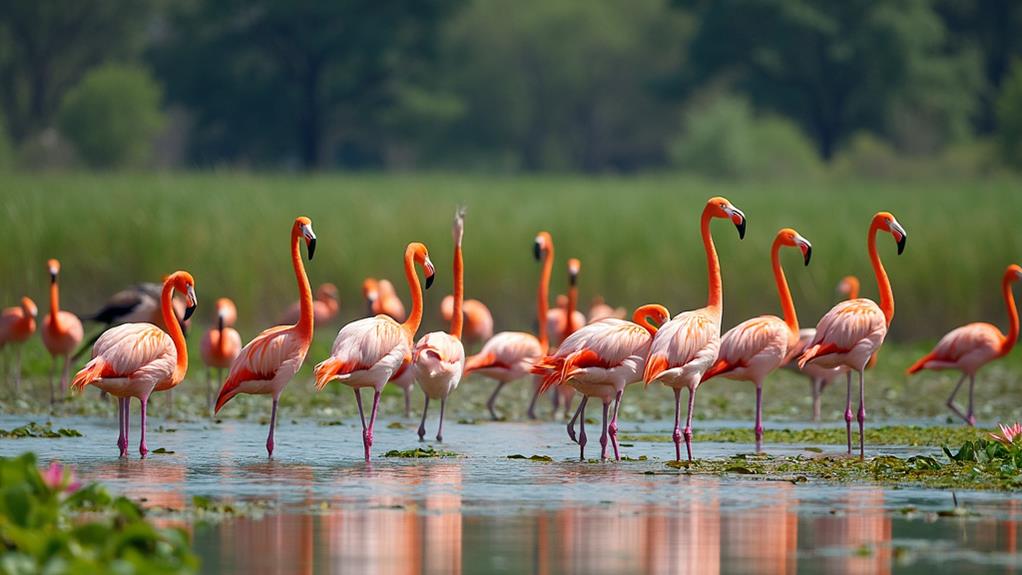

Flamingos are crucial for wetland ecosystems. Their feeding habits stir up sediment, releasing nutrients that support a diverse range of organisms. They control algae populations by filter-feeding, which prevents harmful algal blooms and maintains water quality. Flamingos also regulate small organism populations and disperse seeds and microorganisms through their migration patterns, enhancing biodiversity. Their behavior can indicate the health of their habitats and prompt conservation efforts to protect these environments. By understanding flamingos' roles more deeply, you'll see how important they are to the stability and richness of wetland ecosystems.
Nutrient Recycling
Flamingos play an important role in nutrient recycling within wetland ecosystems. When you observe flamingo feeding, you'll notice they stir up the sediment at the bottom of the water. This action is significant because it releases nutrients trapped in the sediment back into the water column. These nutrients then become available to other organisms, which helps to maintain wetland biodiversity.
As flamingos feed, they filter out small organisms like algae, crustaceans, and plankton from the water. Their unique feeding technique not only provides them with nourishment but also contributes to the overall well-being of the ecosystem. By consuming these organisms, flamingos help to balance the nutrient levels, ensuring that no single species dominates the environment. This balance is critical for supporting a diverse range of plant and animal life.
You might not realize it, but the constant movement and feeding activity of flamingos create an environment where nutrients are continually cycled and redistributed. This process supports the growth of different wetland species, from microorganisms to larger plants and animals. So, the next time you see a flamingo wading through the water, keep in mind that they're doing much more than just looking for food—they're sustaining the entire ecosystem.
Algae Population Control
Managing algae populations is another essential role flamingos play in wetland ecosystems. You might not realize it, but these pink beauties are more than just a pretty sight. Flamingos use specialized feeding strategies to filter algae from the water. By doing so, they help maintain a balance in the ecosystem, preventing harmful algal blooms that can disrupt the habitat and water quality.
Flamingos have a unique way of feeding. They use their beaks to stir up the muddy bottom of wetlands, filtering out algae and small organisms. This process, known as filter-feeding, is highly efficient and allows them to consume large quantities of algae. As they feed, they control the algae population, reducing the risk of algal blooms that can deplete oxygen levels in the water and harm other aquatic life.
Impact on Aquatic Life
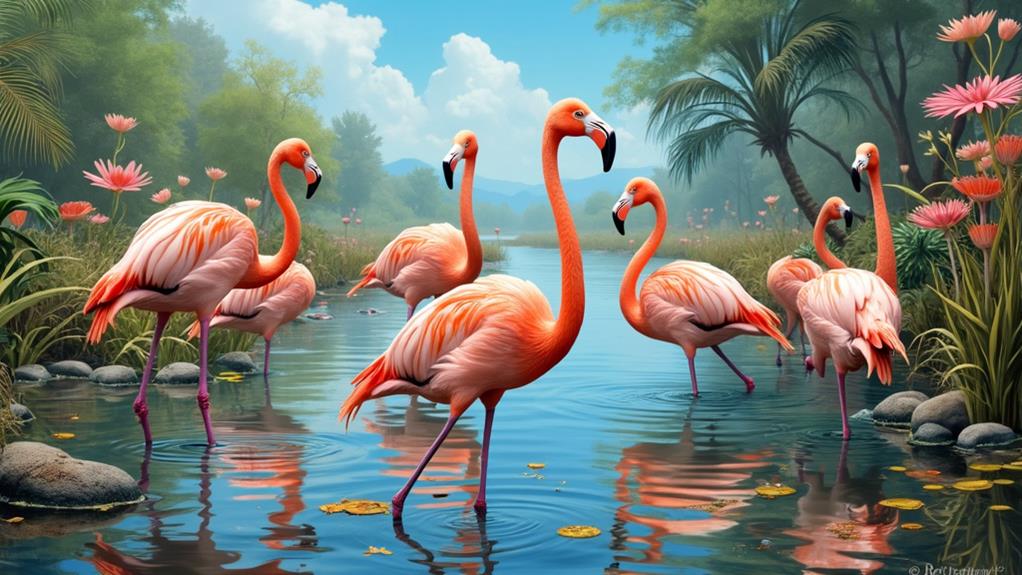

While filter-feeding, flamingos greatly impact the aquatic life within wetland ecosystems. By using their specialized beaks to sift through water, they consume algae, crustaceans, and small organisms. This feeding strategy regulates the population of these species, maintaining a balanced aquatic environment. When you observe flamingo behavior, you'll notice their synchronized movements, which not only improve feeding efficiency but also stir up nutrients, benefiting other aquatic life forms.
Flamingos' migration patterns also play a significant role. As they move between wetlands, they help disperse different plant seeds and microorganisms stuck to their legs and feathers. This natural process supports biodiversity and aids in the colonization of new areas by distinct species. You might not realize it, but these birds act as mobile ecological engineers, shaping the habitats they frequent.
The social dynamics of flamingos further elevate their impact. Large flocks create substantial disturbances in the water, which can prevent certain invasive species from establishing dominance. By understanding these aspects of flamingo behavior, you can appreciate how essential they are to the health and sustainability of wetland ecosystems. Their contributions are crucial and multifaceted, ensuring a thriving aquatic community.
Habitat Health Indicators
The presence and behavior of flamingos offer invaluable insights into the health of wetland ecosystems. By observing these birds, you can gather crucial information about the state of their habitats. Here are four key indicators to watch for:
- Breeding Behavior: When flamingos successfully engage in breeding behavior, it indicates a stable and healthy environment. If you notice that flamingos are nesting and raising chicks, it's a sign that the wetlands provide the necessary resources and conditions for reproduction.
- Migratory Patterns: Flamingos follow specific migratory patterns, and any significant changes in these patterns can signal alterations in the ecosystem. If flamingos start arriving earlier or later than usual, it might indicate shifts in climate or water quality.
- Population Density: The number of flamingos in a given area can tell you a lot about habitat health. A sudden drop in population density could be a red flag for environmental issues like pollution, habitat destruction, or food scarcity.
- Feeding Habits: Observing how and where flamingos feed can provide clues about the availability of food sources. Changes in their feeding habits might suggest shifts in the aquatic life and general health of the wetland.
Conservation Importance
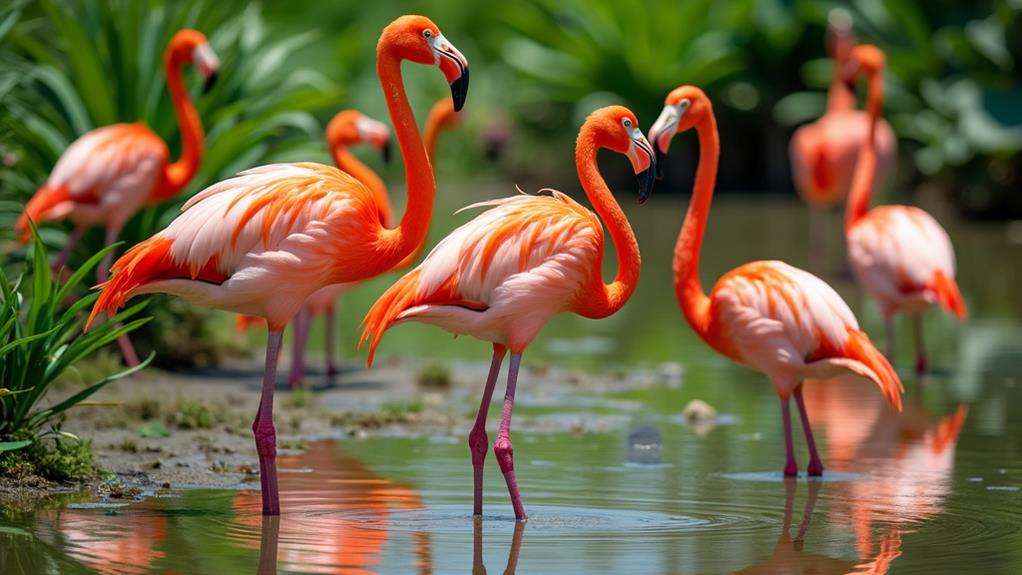

Understanding the conservation significance of flamingos in wetland ecosystems is crucial for maintaining biodiversity. When you protect flamingos, you're also safeguarding a multitude of other species that share their habitat. Flamingos are more than just beautiful birds; their breeding behavior and social structure play a critical role in the health of wetlands.
Flamingos often breed in large colonies, which helps protect their eggs and chicks from predators. This breeding behavior guarantees a higher survival rate for their offspring, contributing to the stability of the population. By conserving areas where flamingos breed, you're also preserving the delicate balance of the ecosystem. These birds' social structure is another important aspect. Flamingos live in large flocks, which help them find food more efficiently and avoid predators. This social structure supports the health of wetland ecosystems by promoting nutrient cycling and vegetation growth.
Without flamingos, the intricate web of life in wetlands could unravel, leading to a decline in biodiversity. By focusing on the conservation of flamingos, you're taking an active step in preserving these crucial ecosystems. Protecting flamingos means protecting wetlands, which benefits countless species, including humans.